Have you ever wondered why you feel sleepy as night falls? The answer lies in a powerful hormone called melatonin.
Understanding how melatonin works can help you take control of your sleep, boost your energy, and improve your overall health. If you’ve been struggling to fall asleep or wake up feeling tired, learning about this natural sleep regulator could be the key to changing your nights—and your days.
Keep reading to discover how melatonin affects your body and how you can use that knowledge to sleep better starting tonight.
Quick Navigation
Melatonin Basics
Understanding melatonin is key to grasping how our body controls sleep. This hormone plays a central role in signaling when it is time to rest. Knowing the basics helps explain why sleep patterns change and how light affects us. Melatonin works quietly but powerfully in the background.
What Is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a natural hormone found in the body. It helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, also called the circadian rhythm. This hormone tells the brain when it is time to sleep and when to wake up. Levels rise in the evening and fall in the morning. This pattern matches the natural day and night cycle.
Melatonin also influences other body functions. It can affect mood, immune response, and body temperature. Because of its role, melatonin is sometimes called the “sleep hormone.”
How Melatonin Is Produced
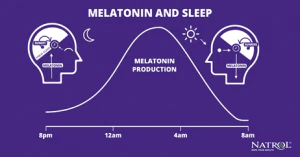
The pineal gland in the brain makes melatonin. This small gland sits deep in the center of the brain. It responds to light signals received from the eyes. When the sun sets and it gets dark, the pineal gland starts producing melatonin.
Light exposure during the day stops melatonin production. This helps the body stay alert and awake. At night, without light, melatonin levels rise and promote sleepiness. This natural rhythm guides our daily sleep patterns.
Role In Sleep Regulation
Melatonin is a natural hormone that helps control sleep. It signals the body when it is time to rest. This hormone plays a key role in managing sleep patterns and timing. Understanding how melatonin works can help improve sleep quality and overall health.
Melatonin And The Circadian Rhythm
The circadian rhythm is the body’s internal clock. It follows a 24-hour cycle, guiding when to be awake and when to sleep. Melatonin levels rise as it gets dark outside. This rise tells the brain that it is night and time to prepare for sleep.
When morning comes, melatonin production drops. This helps the body wake up and feel alert. Light exposure affects melatonin release. Bright light in the morning reduces melatonin, helping reset the internal clock daily.
Impact On Sleep-wake Cycles
Melatonin influences the timing of sleep and wakefulness. It helps people fall asleep faster and improves sleep depth. People with low melatonin may find it harder to fall asleep. Taking melatonin supplements can help adjust sleep patterns.
Shift workers and travelers often experience disrupted sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin can assist in adapting to new schedules or time zones. It supports the body in aligning with new sleep times for better rest.
Factors Affecting Melatonin Levels
Melatonin is a hormone that helps regulate our sleep and wake cycles. Its levels do not stay the same all day. Many factors can change how much melatonin your body makes. These factors affect how well you sleep and feel during the day.
Light Exposure And Melatonin
Light is the strongest signal for melatonin production. Bright light, especially blue light from screens, lowers melatonin levels. Darkness triggers the brain to produce more melatonin. This rise helps you feel sleepy at night. Too much light at night can delay sleep.
Age And Melatonin Production
Melatonin levels change as people age. Children and young adults have higher melatonin production. Older adults often produce less melatonin. This drop can cause trouble falling asleep. Age affects the natural rhythm of melatonin release.
Lifestyle Influences
Daily habits impact melatonin levels. Stress and irregular sleep times can lower melatonin. Eating heavy meals late at night may interfere with production. Exercise, especially during the day, can help normalize melatonin rhythms. Consistent routines support steady melatonin levels.
Melatonin Supplements
Melatonin supplements are widely used to support sleep and regulate the body’s internal clock. These supplements contain synthetic melatonin, a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland. People take melatonin supplements to improve sleep quality and manage sleep disorders.
Melatonin supplements come in various forms such as tablets, capsules, gummies, and liquids. They are available over the counter in many countries. Understanding their uses, proper dosage, and possible side effects helps in using them safely and effectively.
Common Uses And Benefits
Melatonin supplements help people fall asleep faster. They are often used by those with insomnia or jet lag. Shift workers also use melatonin to adjust their sleep schedules. Some studies suggest melatonin may reduce anxiety before surgery. It can improve overall sleep quality and duration. Melatonin supports the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Dosage And Timing
The usual melatonin dose ranges from 0.5 mg to 5 mg. Taking the supplement 30 to 60 minutes before bedtime works best. Smaller doses can be effective and reduce side effects. It is important to follow the instructions on the product label. Melatonin should not be taken too late at night. Consistent timing helps the body adjust to the supplement.
Potential Side Effects
Melatonin supplements are generally safe for short-term use. Some people may experience dizziness or headaches. Mild nausea or sleepiness can also occur. Rarely, melatonin may cause vivid dreams or irritability. Long-term effects are still not fully known. Always talk to a doctor before starting melatonin, especially for children or pregnant women.
Melatonin Beyond Sleep
Melatonin is famous for helping people sleep. It signals the body to rest at night. But melatonin does much more than support sleep. It also plays important roles inside the body that many people do not know about. These roles help keep the body healthy and strong.
Antioxidant Properties
Melatonin acts as a powerful antioxidant. It fights harmful molecules called free radicals. Free radicals can damage cells and cause aging. Melatonin helps neutralize these molecules before they harm the body. This protects cells and supports overall health. Its antioxidant power helps reduce inflammation, too. This effect benefits many parts of the body, from the brain to the heart.
Role In Immune Function
Melatonin supports the immune system’s defense. It helps the body recognize and fight infections. Melatonin guides immune cells to where they are needed most. It also helps reduce harmful inflammation during illness. This keeps the immune response balanced and effective. A strong immune system means better protection from colds and other diseases.
Optimizing Natural Melatonin
Optimizing natural melatonin helps improve sleep quality. This hormone controls your sleep and wake cycles. Boosting your body’s melatonin naturally supports better rest. Simple changes can increase melatonin production without supplements. Focus on daily habits and environment for best results.
Improving Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep hygiene means a regular sleep schedule. Go to bed and wake up at the same time. Avoid caffeine and heavy meals before bedtime. Create a calm and quiet bedroom space. Keep your bedroom cool and dark for better sleep.
Managing Light Exposure
Light controls melatonin production. Bright light during the day increases alertness. Dim lights in the evening signal your body to prepare for sleep. Avoid screens at least one hour before bed. Use blackout curtains to block outside light at night.
Diet And Melatonin Production
Certain foods can help your body make melatonin. Eat foods rich in tryptophan, like turkey and nuts. Include fruits like cherries and bananas in your diet. Avoid heavy or sugary meals late at night. Drink herbal teas like chamomile to relax before bed.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Melatonin And How Does It Work?
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland. It regulates the sleep-wake cycle by signaling the brain when it’s time to sleep. Levels rise in the evening and fall in the morning, helping to maintain a healthy circadian rhythm.
How Does Melatonin Affect Sleep Quality?
Melatonin improves sleep quality by promoting faster sleep onset and deeper rest. It helps reset the body’s internal clock, especially after jet lag or shift work. This hormone supports consistent sleep patterns and reduces insomnia symptoms naturally.
Can Melatonin Supplements Help With Insomnia?
Yes, melatonin supplements can aid insomnia by mimicking natural hormone levels. They are most effective for short-term use and specific sleep disorders. However, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended before starting supplements to ensure safety and proper dosage.
How Long Does Melatonin Take To Work?
Melatonin usually takes about 30 minutes to one hour to start working. Timing is important; taking it too late or early can disrupt the sleep cycle. Proper use helps align the body’s internal clock for better sleep.
Conclusion
Melatonin helps your body know when to sleep and wake. It controls your internal clock by rising at night and falling in the day. This natural hormone supports good sleep patterns and overall health. Understanding how melatonin works can guide better sleep habits.
Simple changes, like reducing light before bedtime, can boost its effect. Sleep well, feel better, and let melatonin do its job.


