Have you ever wondered why you struggle to fall asleep after scrolling on your phone at night? The answer might be closer than you think—right in the light around you.
Light exposure plays a powerful role in controlling your sleep patterns. Understanding how different types of light affect your body can help you take control of your nights and wake up feeling refreshed. Keep reading to discover simple changes you can make to improve your sleep by managing light exposure effectively.
Quick Navigation
Role Of Light In Sleep Regulation
Light plays a key role in controlling how we sleep. Our bodies rely on light signals to know when to feel awake and when to rest. This helps keep our sleep schedule steady and healthy.
Changes in light during the day tell our brain to adjust sleep patterns. This natural process makes sure we sleep at night and stay alert during the day.
Circadian Rhythm And Light
The circadian rhythm is our body’s internal clock. It runs on a roughly 24-hour cycle. Light helps reset this clock every day.
Morning light sends a strong signal to wake up. It tells the brain that it is time to be active. Evening darkness signals the brain to prepare for sleep.
Too much light late at night can confuse this clock. It may delay sleep and cause tiredness the next day.
Melatonin Production And Light Exposure
Melatonin is a hormone that helps us fall asleep. Our body makes more melatonin when it is dark. Light exposure can lower melatonin levels.
Bright light in the evening can stop melatonin production. This makes falling asleep harder. Using dim lights before bed supports natural melatonin release.
Good sleep depends on a balance of light and darkness. Managing light exposure helps keep melatonin levels healthy.
Types Of Light And Their Effects
Light affects our sleep in many ways. Different types of light change how our body feels and works. Some light helps us feel awake and alert. Other light can make us sleepy or restless. Understanding these types helps us improve our sleep.
Our body clock reacts to light. It tells us when to wake up and when to rest. The type of light we see can speed up or slow down this clock. Below are the main types of light and their effects on sleep.
Natural Sunlight
Natural sunlight is the best light for our body clock. It contains all colors of light, including blue light. Morning sunlight helps reset our internal clock. It boosts mood and energy for the day. Getting sunlight during the day improves sleep quality at night.
Artificial Light Sources
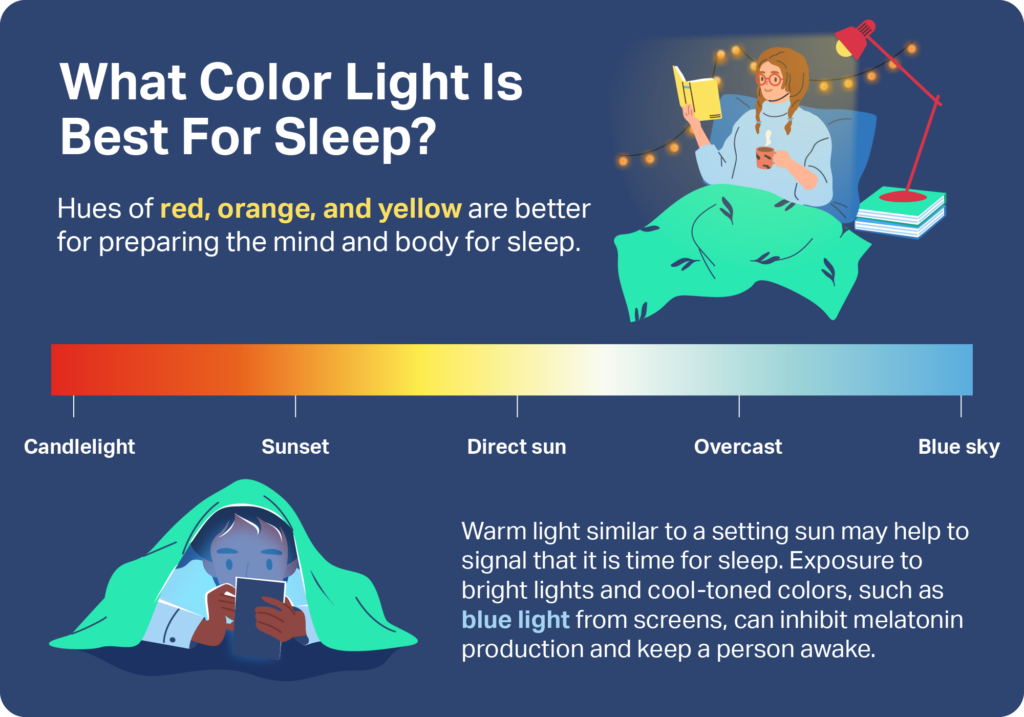
Artificial lights come from bulbs, lamps, and screens. They often lack the full spectrum of natural light. Some artificial lights are very bright and can confuse our body clock. Light at night from these sources can delay sleep. Using dim, warm-colored lights in the evening helps prepare the body for rest.
Blue Light Impact
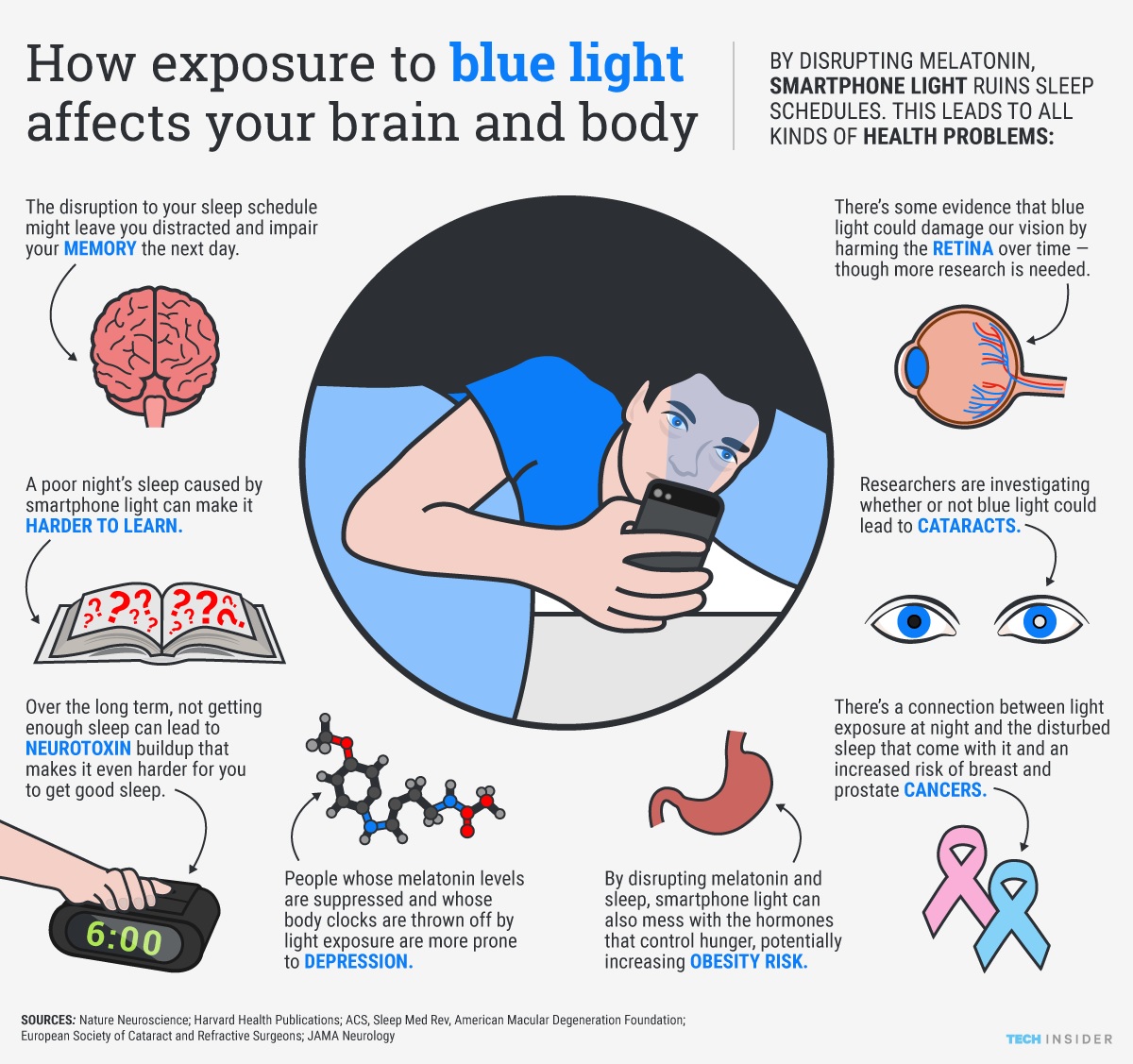
Blue light is a strong signal for our brain to stay awake. It is found in sunlight and many screens. Exposure to blue light at night stops melatonin, the sleep hormone. This makes it harder to fall asleep and reduces sleep quality. Reducing screen time before bed limits blue light impact and supports better sleep.
Daytime Light Exposure Benefits
Daytime light exposure plays a key role in improving sleep quality. Natural light helps the body stay active and alert during the day. It also sets the internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep at night. Spending time outside or near windows can bring many health benefits. Bright light during the day boosts energy and mood. It also helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, supporting better rest.
Boosting Alertness And Mood
Bright light during the day increases alertness. It helps reduce feelings of tiredness and drowsiness. Exposure to sunlight triggers the release of serotonin. This hormone improves mood and creates a sense of well-being. People who get enough light tend to feel happier. This can lower the risk of depression and anxiety. A simple walk outside can lift spirits and sharpen focus.
Strengthening Sleep-wake Cycle
Daylight exposure supports the body’s natural clock. This clock tells the body when to sleep and when to wake. Light signals the brain to stay awake during the day. It also prepares the body to feel sleepy at night. Without enough light, the sleep-wake cycle can become confused. Regular exposure to daylight helps keep this cycle steady. This leads to deeper and more restful sleep at night.
Evening Light And Sleep Disruption
Evening light plays a big role in how well people sleep. Light exposure at night can confuse the body’s natural clock. This clock, called the circadian rhythm, tells the body when to feel awake or sleepy. Bright light in the evening can delay this clock. It makes falling asleep harder and reduces sleep quality.
Many people use devices that emit light before bed. Understanding how this light affects sleep can help improve rest and overall health.
Screen Time And Sleep Quality
Screens give off blue light that tricks the brain. This light signals the brain to stay awake. Using phones, tablets, or computers late at night can delay sleep. It lowers the production of melatonin, the hormone that helps people fall asleep.
Long screen time before bed leads to poor sleep quality. People may feel tired but find it hard to rest deeply. Turning off screens at least one hour before bed helps improve sleep.
Light Intensity And Timing
The brightness of light in the evening affects sleep differently. Bright lights have a stronger effect on the body clock. Dim lights cause less disruption to sleep patterns.
Timing of light exposure is also important. Light close to bedtime has a bigger impact than light earlier in the evening. Reducing light intensity and avoiding bright lights after sunset can improve sleep.
Improving Sleep Through Light Management
Managing light exposure plays a big role in improving sleep. Our bodies use light signals to control the sleep-wake cycle. Proper light management helps the brain know when to feel awake and when to get ready for sleep. Simple changes in light habits can lead to better rest and more energy during the day.
Optimizing Daylight Exposure
Natural daylight helps set the body’s internal clock. Spend time outside in the morning or early afternoon. Bright sunlight reduces sleepiness and boosts alertness. Open curtains wide to let sunlight into rooms. This exposure helps the brain stay on a healthy sleep schedule.
Limiting Evening Light
Bright light at night confuses the body. It signals that it is time to be awake. Avoid screens and bright bulbs at least one hour before bed. Use dim, warm lights in the evening. This helps the brain produce melatonin, the hormone that makes you sleepy.
Using Light Therapy Devices
Light therapy devices can help reset the sleep cycle. They are useful for those with sleep problems or shift work. Use a light box with bright, white light for 20-30 minutes in the morning. This helps improve mood and alertness. Always follow device instructions for safe use.
Practical Tips For Better Rest
Good sleep starts with the right habits and environment. Light exposure plays a big role in how well you rest. Small changes can help your body relax and prepare for sleep. Follow these practical tips to improve your rest every night.
Bedroom Lighting Setup
Use dim lights in the evening. Bright lights can stop your body from making melatonin, the sleep hormone. Choose warm-colored bulbs for your bedroom. Avoid blue or white lights before bed. Blackout curtains help block outside light. Keep your room dark for better sleep quality.
Bedtime Routine Adjustments
Start winding down 30 minutes before bed. Lower the lights and do calm activities like reading. Avoid strong light sources during this time. Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time daily. Your body will get used to a natural rhythm. This helps improve sleep consistency.
Technology Use Guidelines
Turn off screens at least one hour before sleep. Phones, tablets, and computers emit blue light that harms melatonin. Use night mode or blue light filters if needed. Keep devices out of reach to avoid temptation. Instead, focus on relaxing activities before bed.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Light Exposure Impact Sleep Quality?
Light exposure influences sleep by regulating melatonin production. Bright light at night reduces melatonin, delaying sleep onset. Proper light during the day supports a natural sleep-wake cycle, improving overall sleep quality and duration.
What Type Of Light Disrupts Sleep The Most?
Blue light, emitted by screens and LED bulbs, disrupts sleep the most. It suppresses melatonin more strongly than other light types, making it harder to fall asleep and reducing sleep quality.
When Should You Avoid Light For Better Sleep?
Avoid bright and blue light at least one hour before bedtime. This helps melatonin levels rise naturally, promoting quicker sleep onset and deeper rest throughout the night.
Can Morning Light Exposure Improve Sleep Patterns?
Yes, morning light exposure helps reset the circadian rhythm. It signals your body to wake up and boosts alertness, leading to better sleep timing and improved sleep quality at night.
Conclusion
Light exposure plays a big role in how well you sleep. Bright light during the day helps your body stay awake and alert. Dim light in the evening tells your brain to prepare for rest. Avoid screens and bright lights before bed to fall asleep faster.
A regular light routine can improve your sleep quality. Small changes in light habits make a big difference. Sleep better by paying attention to light around you. Simple steps lead to peaceful, refreshing nights.


