Have you ever wondered if your body can really get used to losing sleep night after night? Maybe you’re pushing through long workdays or juggling endless responsibilities, thinking you’ll just adapt over time.
But what if that feeling of being tired all the time isn’t something you can simply get used to? You’ll discover the surprising truth about chronic sleep deprivation and how it affects your mind and body in ways you might never expect.
Keep reading—you owe it to yourself to know what’s really happening when you miss out on sleep.

Quick Navigation
Effects Of Chronic Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation affects more than just feeling tired. It harms the body and mind in many ways. Over time, the lack of sleep can lead to serious health problems. Understanding these effects helps show why good sleep is vital for well-being.
Physical Health Consequences
Sleep loss weakens the immune system. This makes the body less able to fight infections. It also raises the risk of heart disease and high blood pressure. Weight gain and diabetes risk increase without enough sleep. The body struggles to repair itself during rest. Chronic sleep deprivation can cause persistent fatigue and muscle pain.
Mental Health Impact
Sleep loss harms emotional health. It can cause anxiety and depression. Mood swings become more frequent with poor sleep. People often feel more stressed and irritable. Lack of sleep reduces the ability to cope with daily problems. This creates a cycle of worsening mental health and poor sleep.
Cognitive Decline Risks
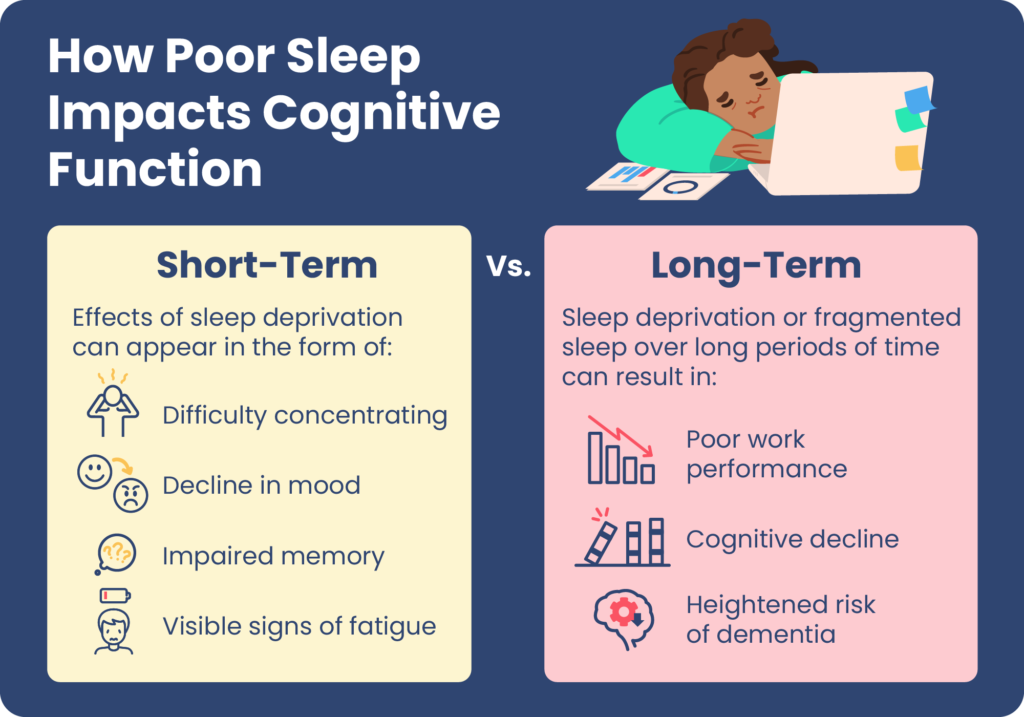
Sleep is essential for brain function. Without enough rest, memory suffers. Learning new things becomes harder. Attention and concentration decrease. Decision-making skills weaken over time. Chronic sleep deprivation may increase the risk of dementia. The brain needs sleep to clear waste and stay healthy.
Body’s Response To Sleep Loss
Sleep loss affects the body in many ways. The body tries to adjust to less sleep. Some changes happen quickly. Others take longer and cause harm. Understanding these responses helps explain why sleep is important.
Short-term Adaptations
The body reacts fast to sleep loss. It increases stress hormones like cortisol. This helps keep you awake and alert. Your heart rate may rise. You might feel more awake for a while. But energy drops after some time. The brain also changes its activity. It tries to focus despite tiredness. These changes help you function briefly.
Long-term Damage
Chronic sleep loss causes serious harm. It weakens the immune system. You get sick more often. Memory and thinking skills decline. Mood problems like anxiety and depression appear. Risk of heart disease and diabetes rises. The body’s repair systems slow down. Long-term sleep deprivation is dangerous for health.
Sleep Debt And Recovery
Missed sleep adds up as sleep debt. The body tries to pay it back later. Extra sleep helps restore energy and brain function. But full recovery can take days. Sleeping longer on weekends is common. It reduces some effects but not all. Regular good sleep is best for recovery.
Can You Truly Adapt?
Many people wonder if the body can truly get used to chronic sleep deprivation. The idea of adapting to less sleep sounds hopeful. Yet, the reality is more complex. Understanding how the body responds to sleep loss helps clear up common myths. It also reveals how science views habitual sleep deprivation. Individual differences play a big role too. Here is a closer look at whether you can truly adapt to chronic sleep deprivation.
Myths About Sleep Adaptation
One common myth says people can train their bodies to need less sleep. Some believe sleeping fewer hours will make them more productive. Others claim they feel fine after several nights of little sleep. These ideas often come from wishful thinking. The truth is the body still needs enough rest to function well. Feeling alert does not mean the brain is fully recovered. Many people underestimate the harm caused by ongoing sleep loss.
Scientific Findings On Habitual Sleep Loss
Studies show chronic sleep deprivation harms memory, focus, and mood. The brain cannot fully adjust to losing sleep regularly. Performance drops even if a person feels okay. Research proves sleep debt builds up over time. It causes slower reaction times and weakens the immune system. Science also finds it increases risks for heart disease and diabetes. No amount of practice can erase these effects. Sleep is essential for physical and mental health.
Individual Differences In Tolerance
People vary in how much sleep they need. Genetics influence sleep patterns and resilience to loss. Some may handle short sleep better than others. Still, most adults require 7 to 9 hours each night. Those with less tolerance face faster decline in alertness. Personal habits and stress levels also affect sleep needs. Even so, no one is immune to the dangers of chronic sleep deprivation. It is best to listen to your body’s signals.
Signs You’re Suffering
Chronic sleep deprivation can sneak up on anyone. The signs are not always easy to spot. Many people think they just feel tired. But there are clearer signals your body gives when it lacks rest. Recognizing these signs helps you understand how serious the problem is.
Sleep loss affects more than just your energy. It changes how your body and mind work every day. Knowing the signs can help you take action before it gets worse.
Warning Symptoms
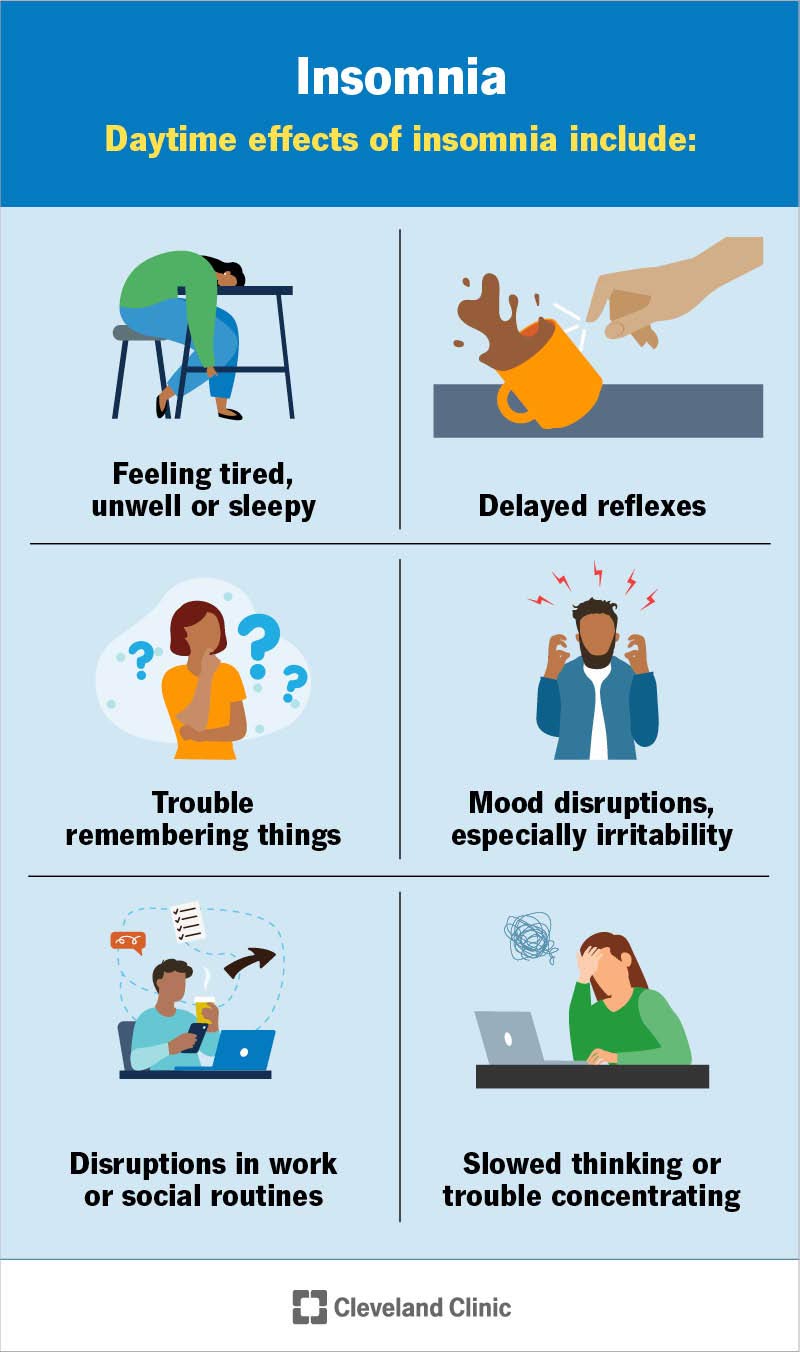
Feeling tired all the time is a common sign. You might also notice trouble focusing or remembering things. Mood changes like irritability or sadness can appear. Your reaction time slows down, making simple tasks harder. Sometimes, headaches or constant yawning occur. These symptoms warn your body needs more sleep.
Impact On Daily Performance
Sleep loss lowers your work quality and speed. You may miss details or make careless mistakes. Driving or operating machines becomes dangerous. Social interactions might feel harder or awkward. Physical strength and coordination decrease, affecting exercise or chores. Overall, daily activities become more difficult and tiring.
Hidden Risks
Long-term sleep deprivation harms your health deeply. It raises the chance of heart disease and diabetes. Immune system weakens, making you catch illnesses easier. Mental health problems like anxiety and depression grow. Weight gain and hormone imbalance may happen too. These hidden dangers show sleep is vital for life.
Strategies To Combat Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation can harm your body and mind. Finding ways to fight tiredness helps you stay healthy and alert. Use simple methods to improve your sleep and feel better during the day.
Try different strategies to reduce the effects of poor sleep. Small changes can make a big difference in how you function daily.
Improving Sleep Hygiene
Keep a regular bedtime and wake-up time. Your body learns when to sleep and when to wake. Avoid screens like phones and TVs one hour before bed. Bright lights confuse your brain and delay sleep. Make your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool. These conditions help your body relax and fall asleep faster.
Napping And Rest Techniques
Short naps can boost your energy and focus. Limit naps to 20-30 minutes to avoid feeling groggy. Find a quiet place to rest during the day. Deep breathing or meditation also helps calm your mind. Resting your eyes for a few minutes can reduce tiredness.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Exercise regularly but not too close to bedtime. Physical activity helps you fall asleep faster. Avoid caffeine and heavy meals late in the day. These can keep you awake at night. Manage stress through relaxation or talking with friends. A calm mind supports better sleep quality.
When To Seek Help
Chronic sleep deprivation can harm your body and mind over time. Knowing when to seek help is crucial. It can stop serious problems before they start. Watch for signs that your sleep issues need professional care. Early action can improve your quality of life.
Recognizing Sleep Disorders
Sleep problems may not be just tiredness. Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can signal a disorder. Loud snoring, gasping during sleep, or feeling very sleepy during the day are red flags. Restless legs or sudden body movements at night also matter. These signs show it is time to see a doctor.
Professional Treatment Options
Doctors can diagnose sleep disorders with tests and interviews. Treatments vary from simple lifestyle changes to medical devices or medicines. For example, CPAP machines help people with sleep apnea breathe better. Cognitive-behavioral therapy can improve insomnia by changing thoughts and habits. Professionals tailor treatments to fit your needs.
Long-term Health Monitoring
Chronic sleep deprivation can cause heart disease, diabetes, and memory loss. Regular check-ups help track these risks. Doctors monitor blood pressure, blood sugar, and mental health over time. Keeping an eye on these factors helps prevent serious illness. Long-term care supports your overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Chronic Sleep Deprivation Become A Habit?
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation can become a habit. Over time, your body adjusts to less sleep but still suffers cognitive and health issues.
Does The Body Fully Adapt To Less Sleep?
No, the body never fully adapts to reduced sleep. Performance, memory, and immune function decline with ongoing sleep loss.
What Are The Long-term Effects Of Sleep Deprivation?
Long-term sleep deprivation increases risks of heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and mental health disorders. It also impairs brain function.
Can You Recover From Chronic Sleep Deprivation?
Partial recovery is possible with extended rest, but some damage to cognitive and physical health may persist after long deprivation.
Conclusion
Chronic sleep deprivation feels normal after a while, but it harms your body. Your mind slows down and your health suffers. Restoring good sleep helps you think clearly and feel better. Small changes in your routine can improve sleep quality.
Don’t ignore tiredness or poor sleep habits. Your body needs regular sleep to stay strong and alert. Choose sleep as a priority for a healthier life.


