Have you ever wondered why some people seem to thrive on just a few hours of sleep, while you need a full night to feel rested? The truth is, your sleep needs might be written in your genes.
Understanding these genetic differences can unlock the secret to better rest and more energy every day. If you want to discover how your unique biology shapes your sleep patterns—and how to make the most of it—keep reading. This knowledge could change the way you think about sleep forever.

Quick Navigation
Genetics And Sleep Duration
Sleep needs vary from person to person. Genetics play a key role in how long people sleep. Some people feel rested after six hours. Others need nine or more hours to feel awake. Understanding genetic influence helps explain these differences.
Genes Influencing Sleep Length
Scientists have found specific genes that affect sleep duration. These genes control the body’s internal clock. They help decide when we feel sleepy or awake. Changes in these genes can shorten or lengthen sleep time. This makes some people natural short or long sleepers.
Short Vs Long Sleepers
Short sleepers need less than six hours of sleep. They often feel alert and active. Long sleepers need nine or more hours. They still feel tired if they sleep less. These traits run in families. Genetics strongly influence these sleep patterns.
Impact Of Genetic Variants
Genetic variants affect how our brain controls sleep. Some variants cause people to need less sleep. Others make it harder to wake up early. These differences impact daily energy and mood. Scientists study these variants to learn more about sleep health.
Sleep Quality And Genetic Factors
Sleep quality varies widely from person to person. Genes play a key role in these differences. Some people may feel rested with fewer hours, while others need more. The quality of sleep depends on many genetic factors that affect how deep and restful sleep can be.
Understanding the genetic influence on sleep helps explain why some struggle with tiredness despite adequate sleep time. It also sheds light on why sleep disorders run in families. Exploring these genetic links reveals important insights about sleep health.
Genes Affecting Sleep Architecture
Sleep architecture means the pattern and stages of sleep. Genes influence how long a person stays in each sleep stage. Some genes control the balance between light and deep sleep. These variations affect how refreshed a person feels after sleep. Changes in sleep stages can impact memory, mood, and overall health.
Restorative Sleep And Dna
Restorative sleep allows the body to heal and recover. DNA carries instructions that affect this process. Certain genes regulate brain chemicals that promote deep sleep. These genes also help repair cells and boost immune function during sleep. People with stronger restorative gene activity may feel more energetic and alert.
Genetic Links To Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders often have a genetic basis. Disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome can run in families. Specific gene mutations increase the risk of these conditions. Identifying these genetic factors helps doctors diagnose and treat sleep problems better. Genetics also guide personalized approaches to improve sleep quality.
Personalized Sleep Patterns
Sleep is not the same for everyone. Each person has unique sleep needs that depend on their genetic makeup. Personalized sleep patterns help people understand their natural sleep rhythms. These patterns make it easier to improve sleep quality and overall health.
Chronotypes And Genetic Makeup
Chronotypes are natural sleep-wake preferences. Some people are early birds, waking up with the sun. Others are night owls, feeling active late at night. Genes influence these chronotypes strongly. Specific genes control the body’s internal clock. This clock signals when to sleep and when to wake. Understanding your chronotype helps plan better sleep times.
Tailoring Sleep Schedules
Creating a sleep schedule based on your chronotype improves rest. Early birds benefit from going to bed and waking up early. Night owls feel best sleeping later and waking up late. Tailoring sleep times to genetic needs reduces tiredness. It also boosts mood and concentration during the day.
Adapting To Genetic Sleep Needs
Adapting your lifestyle to fit your genetic sleep pattern is key. Avoid forcing yourself to follow schedules that don’t suit your biology. Adjust work, study, and leisure activities around your best alertness times. Use light exposure to shift your internal clock if needed. Small changes help your body rest fully and recover well.
Genetic Testing For Sleep Insights
Genetic testing offers a new way to understand how our genes affect sleep. It helps reveal why some people need more sleep while others feel fine with less. These tests analyze specific genes linked to sleep patterns and disorders. They provide insights into individual sleep needs and risks for conditions like insomnia or sleep apnea.
Available Genetic Sleep Tests
Several companies offer genetic tests that focus on sleep traits. These tests examine genes related to sleep duration, quality, and circadian rhythms. Some popular tests analyze the PER3 gene, known to influence sleep timing. Others check genes connected to restless leg syndrome or narcolepsy. Many tests use saliva samples for easy DNA collection.
Interpreting Test Results
Test results show variations in genes affecting sleep behavior. They indicate whether you are a “morning person” or a “night owl.” Results may also highlight risks for sleep disorders or how your body processes caffeine. Understanding these results helps tailor better sleep habits. Consulting a sleep specialist can clarify complex findings.
Limitations And Ethical Considerations
Genetic tests cannot predict sleep patterns with full accuracy. Environmental factors like stress and lifestyle still play a big role. Tests also cannot diagnose sleep disorders alone. Privacy concerns arise as genetic data is sensitive information. Always read the privacy policy before sharing your DNA. Ethical use of genetic information is essential for personal safety.
Improving Sleep Based On Genetics
Improving sleep based on genetics means tailoring your habits to fit your unique DNA. Genes influence how much sleep you need and the best times to rest. Understanding these differences helps create better sleep routines.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Genetic traits affect your natural sleep patterns. Adjust your daily routine to match your body’s clock. For example, some people are morning types. Others feel better sleeping late. Align your work and rest times with your genetic sleep needs. Avoid activities that disrupt your natural rhythm. Regular exercise and balanced meals also support healthy sleep.
Sleep Environment Optimization
Your genes can affect sensitivity to light, noise, and temperature. Create a calm bedroom that suits your genetic preferences. Use blackout curtains if light disturbs you. Choose a quiet room or use earplugs to block noise. Keep your room cool and comfortable. Small changes help your body relax and improve sleep quality.
Genetic-informed Therapies
Some therapies work better depending on your genetic makeup. Light therapy can help adjust your internal clock. Melatonin supplements might be more effective for certain genetic profiles. Consult a healthcare provider to find treatments that fit your genes. Personalized therapy can improve sleep and overall health.
Future Of Sleep Genetics
The future of sleep genetics holds promise for better understanding how our genes shape sleep needs. Science is learning more about the links between DNA and sleep patterns. This knowledge could lead to new ways to improve sleep health for everyone.
Advances In Sleep Genomics
Researchers are finding many genes that affect sleep duration and quality. New tools help study large groups of people quickly. This allows scientists to spot small genetic differences linked to sleep. These advances help explain why some people need more sleep than others.
Potential For Personalized Medicine
Genetic information may guide sleep treatments in the future. Doctors could tailor advice based on a person’s unique genetic makeup. This approach might improve sleep disorders and overall well-being. Personalized plans could include specific sleep schedules or therapies.
Challenges Ahead
Many genes influence sleep, making it hard to find clear answers. Environmental and lifestyle factors also affect how we sleep. Ethical concerns arise about using genetic data for sleep care. More research is needed to address these challenges safely and fairly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Genetic Differences In Sleep Needs?
Genetic variations affect sleep duration and quality. Specific genes influence circadian rhythms and sleep homeostasis, shaping individual sleep requirements.
How Do Genes Impact Individual Sleep Duration?
Genes regulate biological clocks and sleep pressure, determining if a person needs more or less sleep to function well.
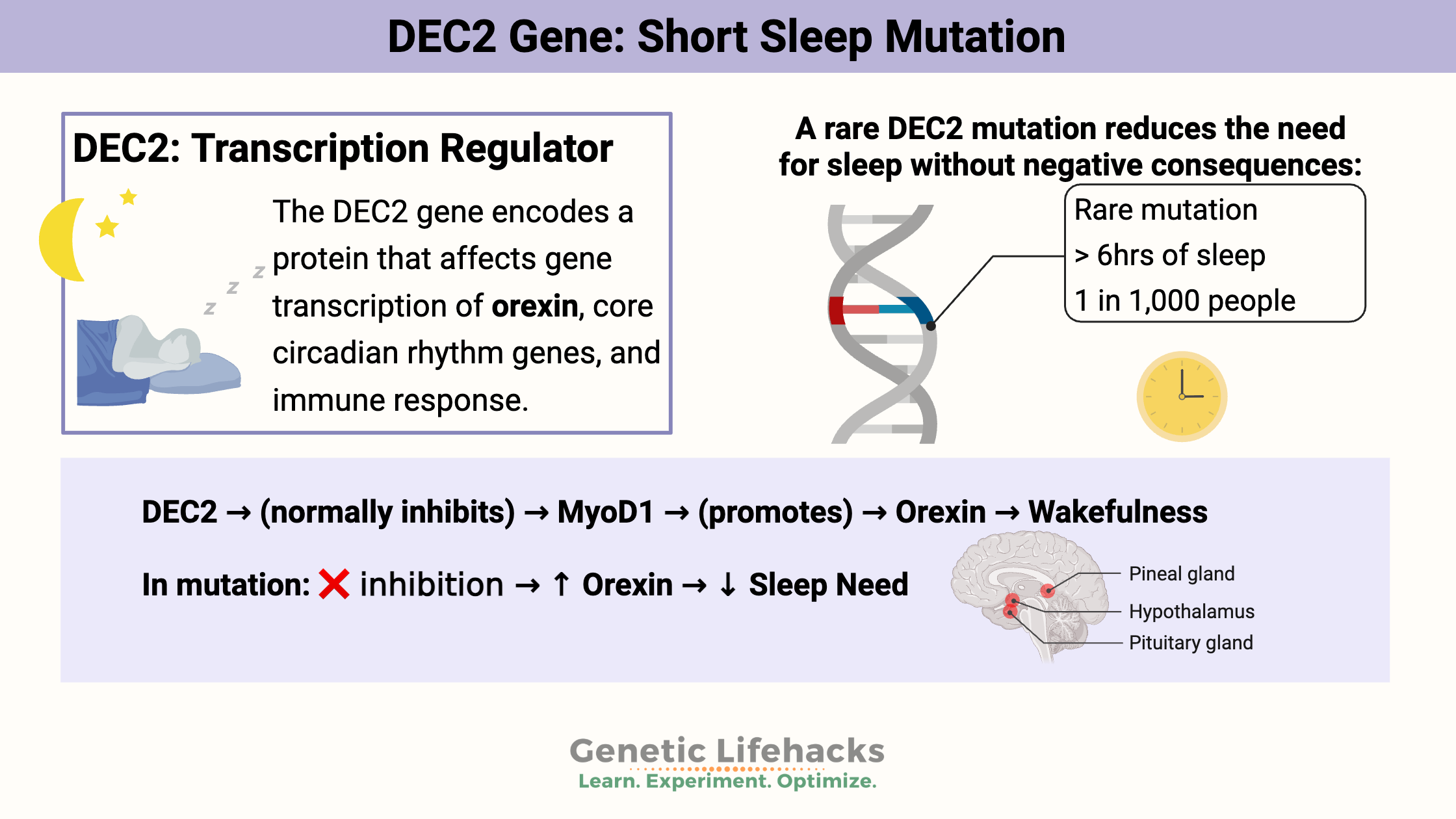
Can Genetic Makeup Explain Why Some Need Less Sleep?
Yes, certain gene variants enable some individuals to thrive on fewer sleep hours without negative effects.
Are Sleep Disorders Linked To Genetic Differences?
Many sleep disorders have genetic components. Variations in sleep-related genes can increase risks of insomnia and other issues.
Conclusion
Genetic differences shape how much sleep each person needs. Some people feel rested with less sleep. Others need more hours to function well. Knowing your unique sleep pattern helps improve health. It reduces tiredness and boosts daily focus. Sleep is not one-size-fits-all.
Respect your body’s signals and rest enough. This understanding supports better habits and well-being. Sleep well, live better.


