Have you ever wondered why you feel sleepy at night and alert during the day? The secret lies deep inside your body—in something called your body clock.
This natural timer controls when you feel awake and when you need rest. Understanding how your body clock works can help you improve your sleep, boost your energy, and feel more in control of your day. Keep reading to discover the fascinating ways your body clock shapes your sleep and wakefulness—and learn simple tips to work with it, not against it.

Quick Navigation
Body Clock Basics
The body clock controls when you sleep and wake up. It helps your body work on a regular schedule. This internal clock adjusts many body functions every day. Understanding the basics of the body clock helps explain sleep patterns. It shows how the body knows when to rest and when to be active.
Circadian Rhythms Explained
Circadian rhythms are natural cycles in the body. They last about 24 hours. These rhythms control sleep, hunger, and energy levels. Your body follows these cycles even without outside cues. They help keep your body balanced and healthy.
Role Of The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a small part in the brain. It acts as the master clock. The SCN sends signals to the rest of the body. It tells your body when to sleep and when to wake. This brain region keeps your circadian rhythms on track.
How Light Influences The Clock
Light is the main cue for the body clock. It enters through your eyes and reaches the SCN. Bright light in the morning resets the clock. It helps you feel awake and alert. Darkness signals your body to prepare for sleep. Light and dark cycles keep your clock in sync.
Sleep-wake Cycle Mechanics
The sleep-wake cycle is the natural pattern of feeling awake and sleepy. It repeats every 24 hours and is controlled by the body clock inside the brain. This cycle helps the body know when to rest and when to be active. Understanding how it works can explain why we feel tired or alert at different times.
The body clock sends signals to the body to prepare for sleep or waking. It works with other systems in the body to keep the cycle steady. Several parts of this process involve hormones and brain activity that change throughout the day and night.
Hormones That Regulate Sleep
Melatonin is the main hormone that tells the body to sleep. The body makes more melatonin as it gets dark. This hormone helps lower body temperature and slow down brain activity. Cortisol, another hormone, rises in the morning. It helps the body wake up and feel alert. These hormones work like signals for the body clock.
Stages Of Sleep And Their Timing
Sleep happens in cycles, each lasting about 90 minutes. There are two main types: REM and non-REM sleep. Non-REM has three stages, starting from light sleep to deep sleep. Deep sleep is important for body repair and growth. REM sleep is when most dreaming happens. The body moves between these stages several times at night.
Interaction Between Body Clock And Sleep Drive
The sleep drive is the body’s need to sleep. It builds up the longer we stay awake. The body clock and sleep drive work together to control sleep timing. The body clock sets when to feel sleepy. The sleep drive pushes the need to rest. This balance keeps sleep regular and helps us feel fresh.
Factors Disrupting The Body Clock
The body clock, also known as the circadian rhythm, controls sleep and wakefulness. It keeps our daily functions in balance. Many factors can disrupt this natural rhythm. Disturbances cause tiredness, poor focus, and mood changes. Understanding these factors helps protect the body clock and improve sleep quality.
Effects Of Jet Lag And Shift Work
Jet lag happens after crossing time zones quickly. The body clock struggles to adjust to the new time. This causes fatigue, insomnia, and irritability. Shift work forces people to work during normal sleep hours. It breaks the natural sleep-wake cycle. Shift workers often feel tired and less alert. Both jet lag and shift work confuse the body clock.
Impact Of Artificial Light Exposure
Artificial light affects the body clock strongly. Light tells the brain when to be awake or sleepy. Exposure to bright screens at night tricks the brain. It delays sleep and reduces sleep quality. Streetlights and indoor lighting also interfere with natural rhythms. Too much artificial light at night can make falling asleep hard.
Lifestyle Habits That Disturb Rhythms
Irregular meal times confuse the body clock. Eating late at night can delay sleep signals. Skipping exercise or exercising too late affects rhythms. Stress and poor sleep habits weaken the body’s natural cycle. Using electronic devices before bed also disrupts sleep. Healthy routines help keep the body clock steady and strong.

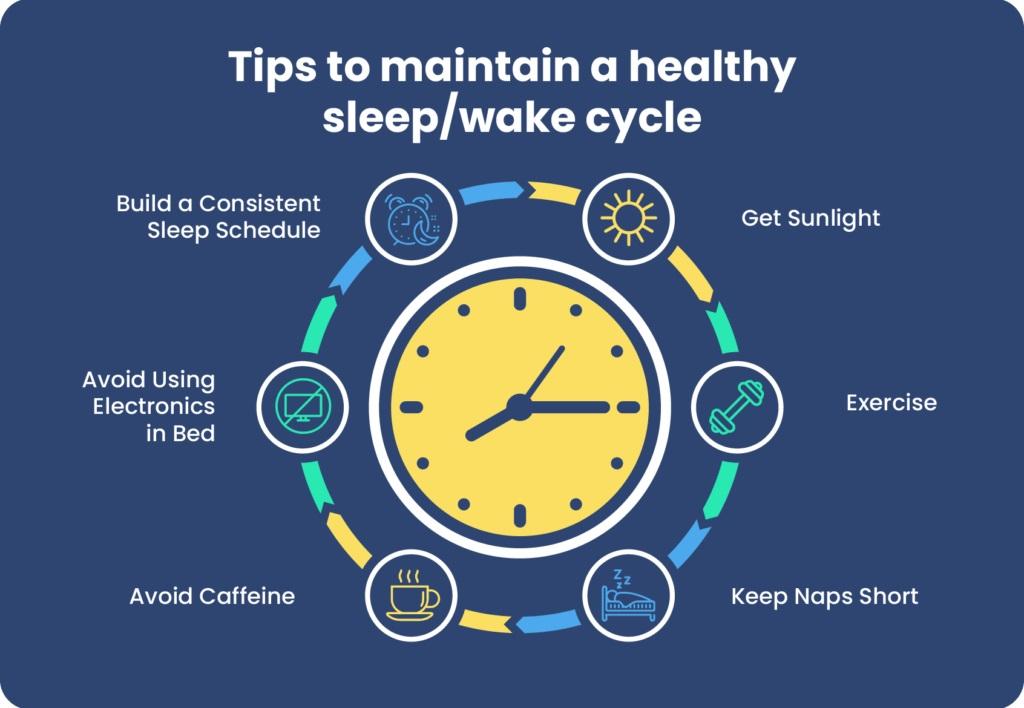
Improving Sleep Through Clock Alignment
Improving sleep starts with aligning your body clock. This natural clock controls when you feel awake or tired. When your clock matches your daily routine, sleep becomes easier and more restful. Small changes can help your body clock stay on track. These changes improve sleep quality and daytime energy.
Optimizing Light Exposure
Light strongly affects your body clock. Bright light in the morning helps wake you up. It tells your brain to be alert and active. Dim light in the evening signals your body to prepare for sleep. Avoid screens and bright lights before bedtime. Natural sunlight during the day supports healthy sleep cycles.
Consistent Sleep Schedules
Going to bed and waking up at the same time helps your clock. This regularity trains your body to expect sleep at certain times. Avoid large changes on weekends or days off. A steady schedule reduces tiredness and improves sleep depth. Consistency strengthens your body’s natural rhythm.
Using Melatonin Wisely
Melatonin is a hormone that controls sleep signals. Supplements can help reset your body clock in some cases. Use melatonin only at the right time, usually before bedtime. Avoid taking it too late or too early. Consult a doctor before starting melatonin to ensure safe use.
Advanced Tips For Better Rest
Better rest depends on more than just sleep duration. Your body clock guides when you feel sleepy and alert. Aligning daily activities with this internal clock improves sleep quality. Small changes in daily habits can lead to deeper, more refreshing sleep.
Timing Meals And Exercise
Eat meals at regular times to support your body clock. Avoid heavy meals late at night to prevent sleep disruption. Exercise boosts sleep but should happen earlier in the day. Evening workouts can raise energy, making it hard to fall asleep.
Creating A Sleep-friendly Environment
Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool for better sleep. Use blackout curtains or eye masks to block light. Remove noise distractions or use white noise machines. Choose comfortable bedding and keep the room tidy to relax your mind.
Tracking And Adjusting Your Sleep Patterns
Monitor your sleep times and quality using a journal or app. Notice patterns in when you feel tired or alert. Adjust your bedtime gradually to match your natural rhythm. Consistency each day helps train your body clock for restful sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Body Clock And How Does It Work?
The body clock, or circadian rhythm, is an internal system regulating sleep and wake cycles. It responds to light and darkness, signaling when to sleep or be awake. This cycle repeats approximately every 24 hours, helping maintain consistent sleep patterns and overall health.
How Does The Body Clock Affect Sleep Quality?
The body clock controls hormone release, like melatonin, which promotes sleep. When aligned properly, it improves sleep quality, making you feel rested. Disruptions to this clock can cause insomnia, fatigue, and poor concentration, highlighting its critical role in healthy sleep.
Why Do We Feel Sleepy At Night According To The Body Clock?
At night, the body clock triggers melatonin production, signaling the brain it’s time to sleep. Darkness increases melatonin, promoting drowsiness. This natural process helps synchronize sleep with night, ensuring restorative rest and supporting overall well-being.
How Can I Reset My Body Clock For Better Sleep?
To reset your body clock, expose yourself to natural light during the day. Avoid bright screens before bedtime and keep a consistent sleep schedule. These habits help realign your circadian rhythm, improving sleep quality and daytime alertness.
Conclusion
The body clock guides when you sleep and wake daily. It keeps your energy steady and mood balanced. Following your natural rhythm helps improve rest and focus. Light and routine both shape this internal timer. Understanding your body clock can boost health and well-being.
Small changes in habits support better sleep patterns. Trust your body’s signals to feel refreshed each day. Sleep well, live well.


