Have you ever wondered what really happens inside your body while you sleep? It’s not just about rest—your hormones are busy making important changes that affect your mood, energy, and overall health.
Understanding these hormonal shifts can help you unlock better sleep and improve how you feel every day. Keep reading to discover the surprising ways your body works behind the scenes during sleep—and how you can use this knowledge to wake up refreshed and balanced.
Quick Navigation
Sleep And Hormone Connection
Sleep and hormones have a close link. Hormones are chemicals in the body that control many functions. Sleep helps the body balance these chemicals. Without good sleep, hormone levels can go out of sync. This affects health and mood.
During sleep, the body repairs itself and sends signals to produce or reduce hormones. This process keeps the body stable and ready for the day. Understanding this connection shows why sleep is so important.
How Sleep Influences Hormone Levels
Sleep controls the timing of hormone release. Most hormones follow a daily rhythm. Sleep triggers the rise or fall of these hormones. For example, some hormones increase at night, while others drop.
Deep sleep stages promote hormone production. Poor sleep reduces hormone output. This can cause problems like tiredness and weight gain. Hormones also affect how well sleep works. It is a two-way street.
Key Hormones Affected By Sleep
Several key hormones change with sleep patterns. Growth hormone, which helps repair tissue, rises during deep sleep. Cortisol, the stress hormone, usually drops at night but rises if sleep is poor.
Melatonin controls the sleep-wake cycle and increases with darkness. Insulin, which manages blood sugar, works better with good sleep. Leptin and ghrelin, hormones that control hunger, also depend on sleep quality.
Growth Hormone Release
Growth hormone plays a key role in the body’s repair and growth during sleep. This hormone helps heal tissues and supports muscle growth. Its release is closely tied to sleep patterns and timing. Understanding how and when growth hormone is released helps explain why good sleep is vital for health.
Timing Of Growth Hormone Secretion
Growth hormone is mainly released during deep sleep stages. The highest secretion happens shortly after you fall asleep. It peaks during the first few hours of sleep. This timing allows the body to focus on repair and growth when resting. Poor sleep or disrupted cycles can lower hormone release.
Role In Tissue Repair And Growth
Growth hormone stimulates tissue repair after daily wear and tear. It helps build muscles and repair skin, bones, and organs. This hormone also boosts protein production, essential for cell growth. Without enough growth hormone, healing slows and recovery takes longer.
Cortisol Fluctuations
Cortisol is a hormone that changes during sleep. It helps control stress and energy in the body. Cortisol levels do not stay the same all night. They go up and down in a pattern that affects how we feel and function.
Cortisol Patterns During Sleep
Cortisol levels usually drop soon after sleep begins. They stay low during deep sleep stages. Near the end of sleep, cortisol rises again. This rise helps prepare the body to wake up. The peak usually happens early in the morning.
This natural cycle is called the cortisol rhythm. It matches the body’s internal clock. The rhythm helps keep energy balanced during the day. Disruptions to this cycle can cause health problems.
Impact On Stress And Metabolism
Cortisol controls how the body handles stress. Low levels at night allow the body to rest and heal. High levels in the morning help face daily challenges.
Cortisol also affects metabolism. It influences blood sugar and fat storage. Proper cortisol patterns support healthy weight and energy use. Irregular cortisol can lead to stress and weight gain.
Good sleep helps keep cortisol levels balanced. Balanced cortisol improves mood, focus, and physical health.
Melatonin Production
Melatonin is a hormone that plays a key role during sleep. It helps the body know when it is time to rest. This hormone is produced in the brain and rises as the day ends. Melatonin signals the body to prepare for sleep and supports deep, restful cycles.
The amount of melatonin changes throughout the night. It peaks in the middle of sleep and drops before waking. This natural rise and fall keep the sleep cycle steady and balanced. Understanding melatonin helps explain why good sleep feels refreshing.
Melatonin’s Role In Sleep Regulation
Melatonin controls the body’s internal clock. It tells the brain when to feel sleepy. This hormone helps shift the body from alertness to rest. Melatonin also improves the quality of sleep by promoting deeper stages. It supports the body’s repair and recovery during the night.
Factors Influencing Melatonin Secretion
Light exposure affects melatonin levels the most. Bright light, especially blue light, stops melatonin production. Darkness triggers the brain to produce more melatonin. Age can change how much melatonin the body makes. Stress and certain medications may lower melatonin levels as well.
Insulin Sensitivity Changes
Insulin sensitivity changes during sleep are crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. This process helps the body use glucose efficiently. Proper insulin function supports energy use and storage. Sleep quality and duration directly affect how well insulin works. Poor sleep can reduce insulin sensitivity, leading to imbalances in blood sugar.
Sleep Effects On Glucose Metabolism
During sleep, the body regulates glucose metabolism to balance energy. Deep sleep phases improve insulin sensitivity, helping cells absorb sugar. Lack of sleep disrupts this process and causes higher blood sugar levels. The hormone cortisol rises with sleep loss, which raises glucose production. This makes it harder for insulin to lower blood sugar.
Implications For Diabetes Risk
Changes in insulin sensitivity during sleep impact diabetes risk significantly. Poor sleep patterns increase the chance of insulin resistance. Insulin resistance means cells do not respond well to insulin. This can lead to type 2 diabetes over time. Consistent, good-quality sleep helps reduce this risk. Prioritizing sleep is a simple way to support metabolic health.
Leptin And Ghrelin Balance
Leptin and ghrelin are two key hormones that regulate hunger and fullness. These hormones work together to keep your appetite in balance. Leptin tells your brain when you have enough energy stored, reducing hunger. Ghrelin signals your body when it is time to eat, increasing appetite. Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining the right balance between these hormones.
Hormones Controlling Appetite
Leptin is produced by fat cells and signals fullness. High leptin levels help reduce food intake. Ghrelin is made in the stomach and stimulates hunger. When ghrelin levels rise, you feel hungry and want to eat. Both hormones send messages to the brain’s appetite center. This system controls how much food you want to eat.
Sleep Impact On Hunger And Satiety
During sleep, leptin levels usually rise, signaling fullness. Ghrelin levels tend to drop, reducing hunger feelings. Poor or short sleep disrupts this balance. Low leptin and high ghrelin cause increased hunger. This imbalance can lead to overeating and weight gain. Good sleep helps keep these hormones balanced and appetite controlled.
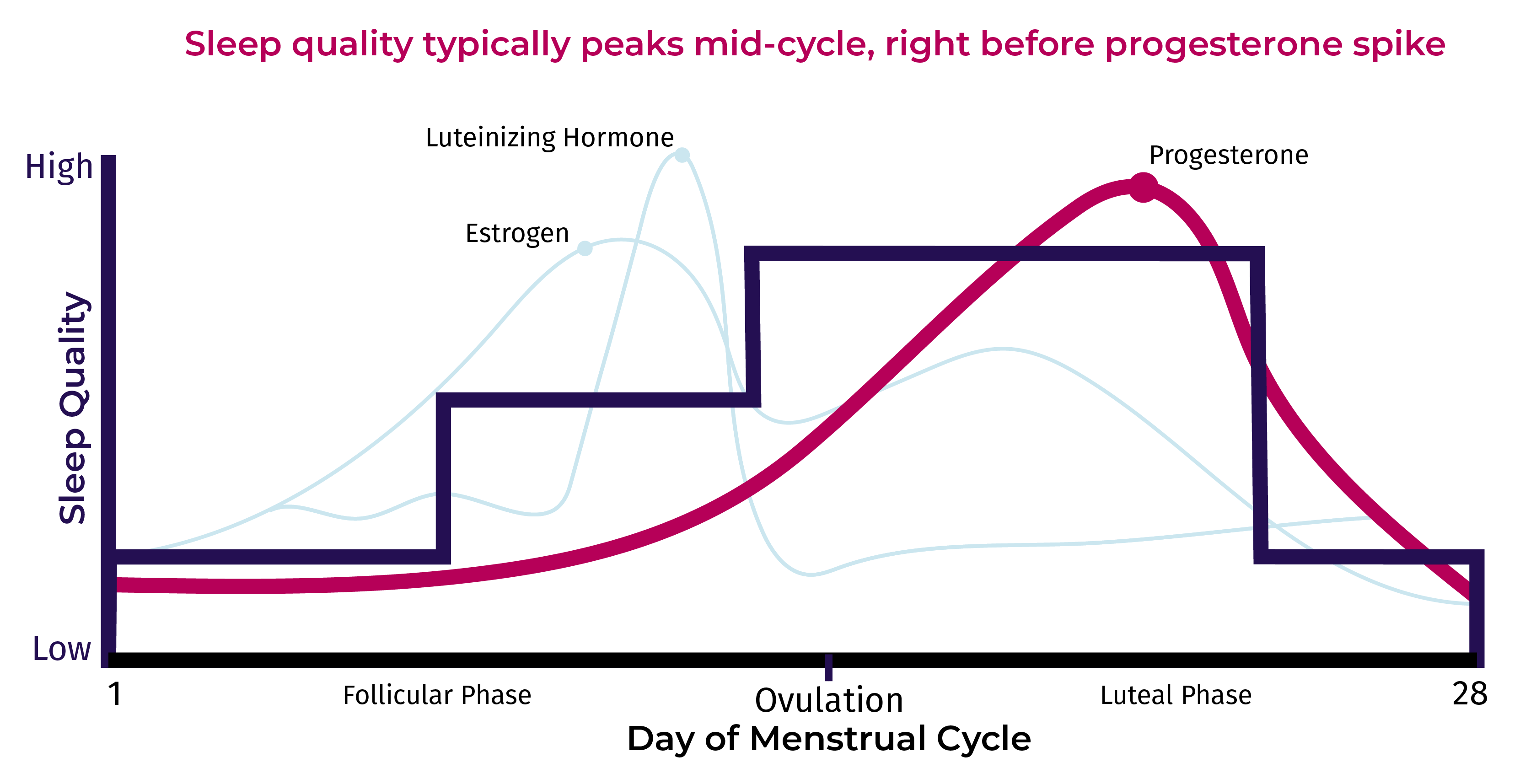
Sex Hormone Variations
Sex hormones change a lot during sleep. These changes help the body rest and repair. Hormones like testosterone and estrogen rise and fall in cycles. This is very important for overall health.
Testosterone Fluctuations During Sleep
Testosterone levels rise mostly during deep sleep. This phase usually happens in the first half of the night. The hormone helps build muscle and maintain energy. Low sleep quality can reduce testosterone production. This may cause tiredness and low mood.
Influence On Reproductive Health
Sex hormones control reproductive functions. Proper sleep keeps these hormones balanced. Imbalance can lead to problems like low fertility or irregular cycles. Good sleep supports hormone release and reproductive health. It helps both men and women stay healthy.

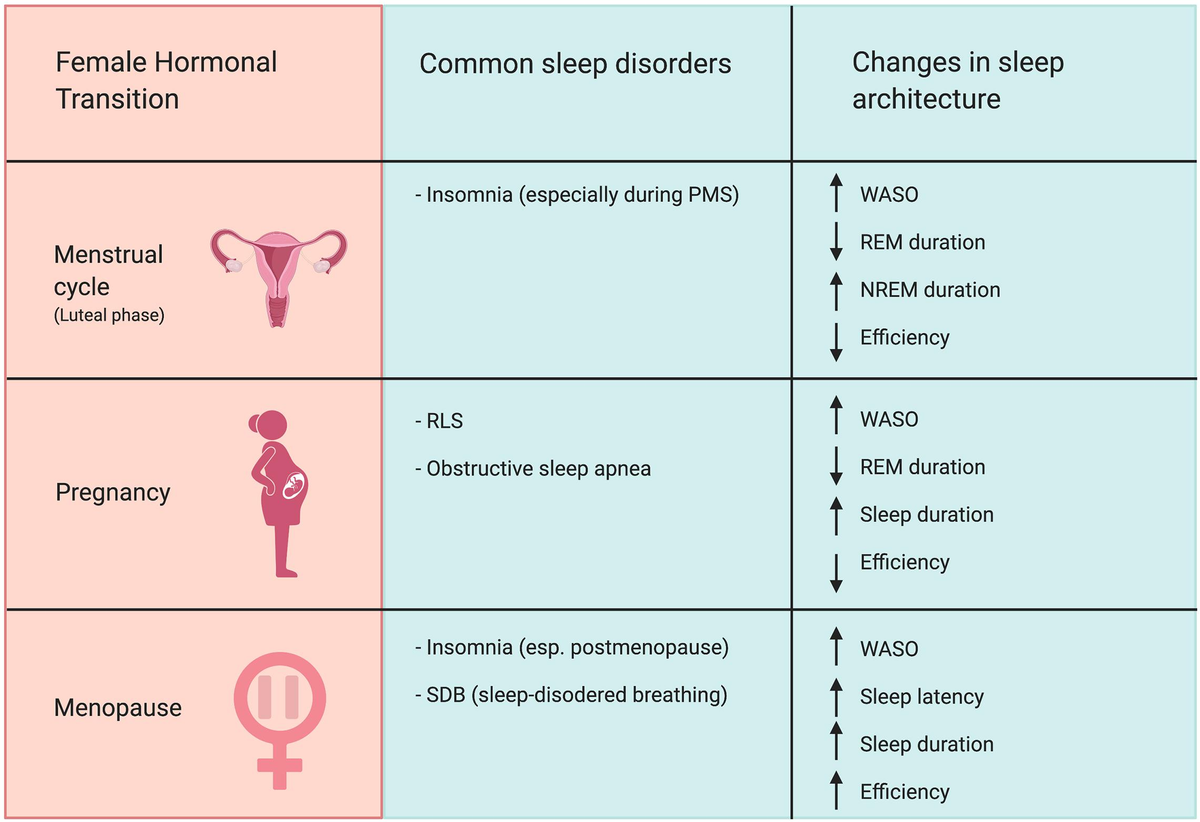
Sleep Disorders And Hormonal Imbalance
Sleep disorders can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body. Hormones control many important functions like growth, mood, and metabolism. When sleep is poor, these hormones get out of sync. This imbalance affects how the body feels and works. Understanding how sleep disorders impact hormones helps manage health better.
Effects Of Poor Sleep On Hormones
Poor sleep lowers the production of growth hormone. This hormone helps with repair and muscle growth. Lack of sleep also raises cortisol, the stress hormone. High cortisol levels cause fatigue and weight gain. Sleep problems reduce insulin sensitivity. This can lead to higher blood sugar levels. Poor sleep also disrupts leptin and ghrelin. These hormones control hunger and fullness. An imbalance may cause overeating and weight gain.
Common Sleep Disorders Impacting Hormones
Sleep apnea is a disorder where breathing stops during sleep. It reduces oxygen flow and disrupts hormone release. Insomnia, the difficulty to fall or stay asleep, raises stress hormones. Restless leg syndrome causes uncomfortable leg movements, leading to poor sleep quality. These disorders interfere with the natural hormone cycle at night. Treating sleep disorders can help restore hormonal balance and improve overall health.
Optimizing Hormone Health Through Sleep
Sleep plays a key role in balancing hormones. It helps the body produce and regulate important hormones. These hormones control mood, energy, growth, and metabolism. Poor sleep can cause hormone imbalances, leading to health problems. Optimizing sleep can support hormone health and improve overall well-being.
Sleep Hygiene Tips
Keep a regular sleep schedule. Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily. Create a calm and dark bedroom environment. Avoid screens and bright lights before bedtime. Limit caffeine and heavy meals in the evening. Try relaxing activities like reading or gentle stretching. These habits help signal your body to prepare for sleep. Better sleep means better hormone regulation.
Lifestyle Changes To Support Hormones
Exercise regularly but not too close to bedtime. Physical activity boosts hormone balance and sleep quality. Manage stress with deep breathing or meditation. Stress raises cortisol, which disrupts sleep and hormones. Eat a balanced diet with proteins, healthy fats, and fiber. Avoid excess sugar and processed foods. Drink enough water throughout the day. These lifestyle changes create a strong foundation for healthy hormones and restful sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Hormones Change During Sleep?
During sleep, key hormones like melatonin, growth hormone, and cortisol fluctuate. Melatonin regulates sleep cycles. Growth hormone supports repair, and cortisol decreases to reduce stress, promoting restful sleep and recovery.
How Does Sleep Affect Hormone Balance?
Sleep helps maintain hormonal balance by regulating secretion patterns. Proper sleep supports metabolism, stress response, and growth. Poor sleep disrupts these processes, leading to imbalances that impact health and well-being.
Why Is Growth Hormone Released During Sleep?
Growth hormone is mainly released during deep sleep stages. It aids tissue repair, muscle growth, and metabolism regulation. This release supports physical recovery and overall body maintenance during restful sleep.
Does Sleep Influence Cortisol Levels?
Yes, cortisol levels drop during early sleep to reduce stress. Levels rise before waking to prepare the body for the day. This natural rhythm helps balance energy and stress responses.
Conclusion
Sleep plays a key role in balancing hormones each night. These changes help your body grow, heal, and stay healthy. Good sleep supports mood, energy, and weight control too. Skipping sleep can disturb this natural process and cause issues. Pay attention to your sleep habits for better hormone health.
Small changes can lead to big benefits over time. Rest well and let your body do its important work. Sleep is more than rest—it’s a time for renewal.


